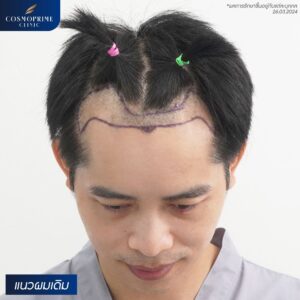
What Is Male Pattern Hair Loss?
Male pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) is the most common cause of hair thinning in men. It is primarily caused by hormonal changes, particularly the androgen hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which affects hair follicles.
Key Characteristics of Male Pattern Hair Loss:
- Receding hairline
- Thinning at the crown
- Gradual progression over time
What Causes Male Pattern Hair Loss?
The primary cause of male pattern hair loss is the hormone DHT. This hormone shrinks hair follicles, shortens the hair growth cycle, and eventually stops new hair from growing.
Main Causes Include:
- Genetics: Family history increases the likelihood of hair loss.
- Hormonal Changes: Increased sensitivity to DHT.
- Age: Hair thinning typically begins in the late 20s or early 30s.
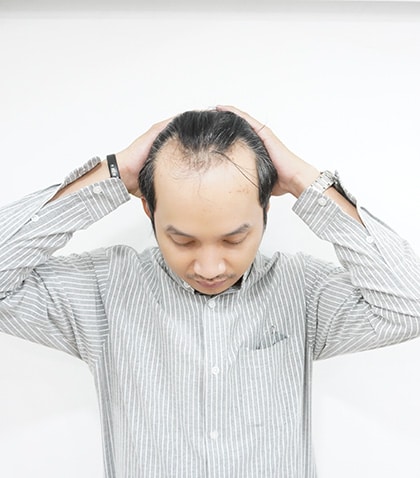

Symptoms of Male Pattern Hair Loss
Recognizing early signs of male pattern hair loss allows for timely intervention.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Receding hairline (M-shaped pattern)
- Thinning at the crown
- Overall hair density reduction
- Increased hair shedding
How to Diagnose Male Pattern Hair Loss
A dermatologist or hair specialist can diagnose male pattern baldness through a physical examination and reviewing your medical history.
Diagnostic Methods:
- Scalp examination
- Family history assessment
- Hair pull test
- Dermoscopy (to assess follicle health)
Treatment Options for Male Pattern Hair Loss
Several treatments are available to slow down or reverse male pattern hair loss.
1. Medications:
- Finasteride: Blocks DHT production to prevent further hair loss.
- Minoxidil: A topical solution that stimulates hair regrowth.
2. Hair Transplant Surgery:
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
3. Advanced Therapies:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Promotes healing and hair regrowth.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Stimulates hair follicles using light energy.