Understanding Hair Loss: An Overview
Hair loss is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it is normal to lose between 50 to 100 strands of hair per day, excessive hair loss can be a cause for concern.
table of contents
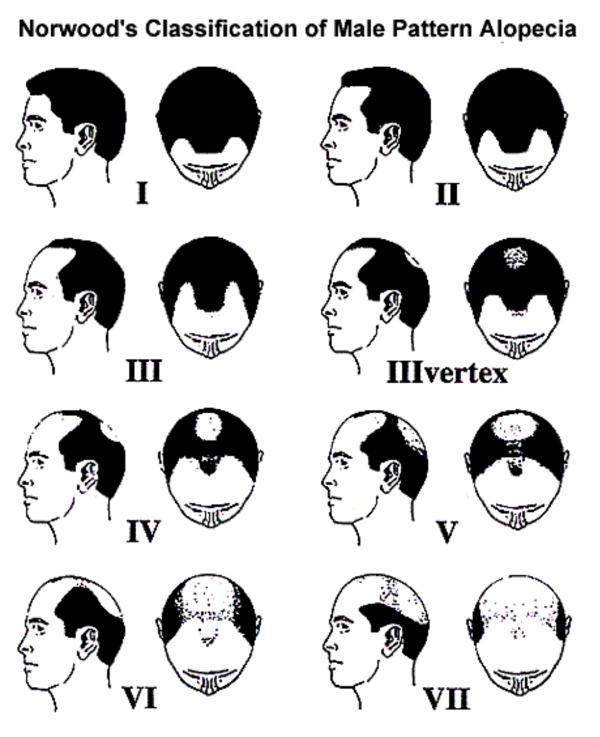
1. Genetic Hair Loss (Androgenetic Alopecia)
Genetic hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss in both men and women. This condition is hereditary and linked to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which causes hair follicles to shrink and eventually stop producing hair.
Symptoms of Genetic Hair Loss:
- Receding hairline (in men)
- Thinning hair around the crown (in women)
- Gradual hair thinning over time
Treatment Options:
- Topical treatments (e.g., minoxidil)
- Oral medications (e.g., finasteride for men)
- Hair transplant surgery

Article written by
Pathompob Khunkitti, MD.
2. Hormonal Changes and Imbalances
Hormonal fluctuations can trigger hair loss. This is common during pregnancy, menopause, or due to thyroid disorders. Elevated levels of DHT in the scalp can also accelerate hair thinning.
Causes of Hormonal Hair Loss:
- Pregnancy and postpartum hormone shifts
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Thyroid hormone imbalance (hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism)
Treatment Options:
- Hormone therapy
- Balancing thyroid levels
- Nutritional support
3. Stress-Related Hair Loss (Telogen Effluvium)
Severe physical or emotional stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to temporary hair loss. This condition, known as telogen effluvium, pushes hair follicles into the resting phase prematurely.
Common Triggers:
- Major surgery or illness
- Emotional stress (e.g., loss of a loved one)
- Sudden weight loss or dietary deficiencies
Treatment Options:
- Stress management techniques
- Balanced diet and supplements
- Regular scalp care
4. Medical Conditions and Illnesses
Certain medical conditions and treatments can result in hair loss. Autoimmune diseases, like alopecia areata, attack hair follicles, causing patchy hair loss.
Medical Causes of Hair Loss:
- Autoimmune disorders (e.g., alopecia areata)
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Scalp infections (e.g., ringworm)
Treatment Options:
- Addressing the underlying condition
- Corticosteroid injections
- Specialized medical treatments
5. Scalp Injuries and Physical Trauma
Injuries to the scalp can damage hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss if untreated. Physical trauma, such as burns or scarring, can prevent hair regrowth.
Causes of Trauma-Induced Hair Loss:
- Burns or wounds on the scalp
- Surgical scars
- Tension from hairstyles (traction alopecia)
Treatment Options:
- Hair restoration surgery
- Scar revision treatments
- Avoiding tight hairstyles
6. Poor Nutrition and Vitamin Deficiency
A lack of essential nutrients can weaken hair and cause shedding. Hair follicles need vitamins and minerals to support healthy growth.
Nutrient Deficiencies Linked to Hair Loss:
- Iron deficiency (anemia)
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Lack of protein
Treatment Options:
- Balanced, nutrient-rich diet
- Supplements (iron, biotin, vitamin D)
- Regular health check-ups
7. Hairstyling Habits and Chemical Damage
Excessive use of heat, harsh chemicals, and tight hairstyles can weaken hair shafts, leading to breakage and hair loss.
Damaging Hair Practices:
- Frequent use of hot tools (e.g., straighteners)
- Chemical treatments (e.g., bleaching, perming)
- Tight braids or ponytails
Treatment Options:
- Reducing heat and chemical exposure
- Using gentle, sulfate-free products
- Regular scalp treatments
When to Seek Professional Help
If you are experiencing persistent hair loss or sudden shedding, it is crucial to consult a hair specialist. Early intervention can prevent further hair loss and restore your confidence.
Signs You Should See a Specialist:
- Sudden, unexplained hair loss
- Patchy or bald spots
- Scalp irritation or inflammation
Contact Cosmo Clinic today to explore personalized hair restoration options tailored to your needs.